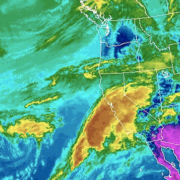
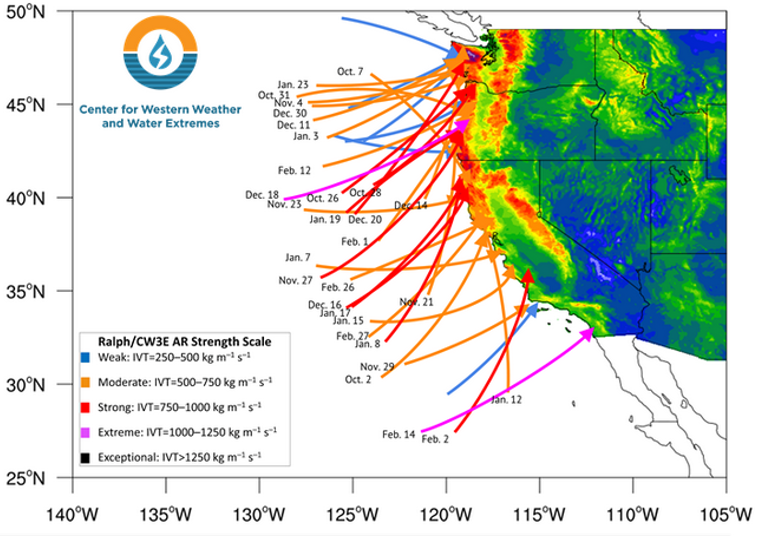
A better understanding and forecasting of atmospheric rivers could improve flood control and water management in California.
The 2019-20 California state budget includes $9.25 million to pay for research into how the state Department of Water Resources can more accurately track the intensity and landfall locations of atmospheric rivers. About half of the state’s annual rainfall and 90 percent of its flooding come from such events.
“Improved forecasting and monitoring of atmospheric river storms would benefit not only California, but the Southwest, in managing our water supply,” said Kelley Gage, director of water resources for the San Diego County Water Authority. “With better forecasting, water managers could also prepare and plan for flooding events caused by the atmospheric rivers.”
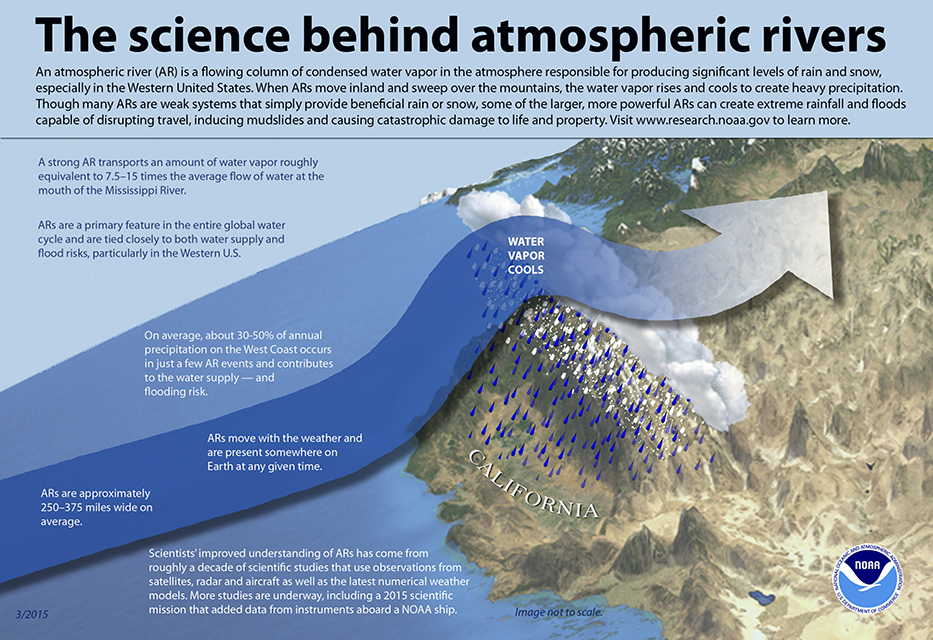
The science behind atmospheric rivers. Graphic: NOAA
Rivers in the sky
Atmospheric rivers are relatively long, narrow regions in the atmosphere – like rivers in the sky – that transport most of the water vapor outside of the tropics, according to NOAA. When the atmospheric rivers make landfall, they release the water vapor in the form or rain or snow.
“The rivers can stretch from 250 to 370 miles wide and carry a water amount more than 7 times the volume of the Mississippi River,” said Alexi Schnell, water resources specialist with the Water Authority.
The research funds were allocated to the Department of Water Resources to “improve observations, forecasts and decisions in support of atmospheric river precipitation events” as part of the DWR’s Research, Mitigation, and Climate Forecasting Program.
Volatile water resources
A new study led by Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego suggests that a new regime of wet and dry extremes is emerging in California. The study shows that the projected increase of extreme precipitation is likely to be caused by streams of moisture in the sky known as atmospheric rivers.
The study was published July 9 in the journal Nature Scientific Reports.
“California already has the most volatile water resources in the country,” according to a news release from Scripps. “Scripps scientists discovered that the state’s precipitation, as it becomes less frequent but preferentially stronger, will vacillate even more wildly between extremes of drought and flooding as a consequence of climate change.”
The federal Bureau of Reclamation, the Southwest Climate Adaptation Science Center, NOAA, the U.S. Geological Survey, and NASA funded the study, “Precipitation regime change in Western North America: The role of Atmospheric Rivers.”
California weather extremes
“As Mediterranean climate regions around the world are becoming more subtropical, the dry season is expanding. California is no exception,” said Alexander Gershunov, a climate scientist at Scripps. “What is exceptional about California is that the heavy precipitation is projected to become more extreme. We knew this from our past work. Now we have identified the mechanism responsible for this bolstering of extremes, and that gives us a more nuanced understanding of what to expect from future hydroclimate and a clearer interpretation of ongoing changes.”
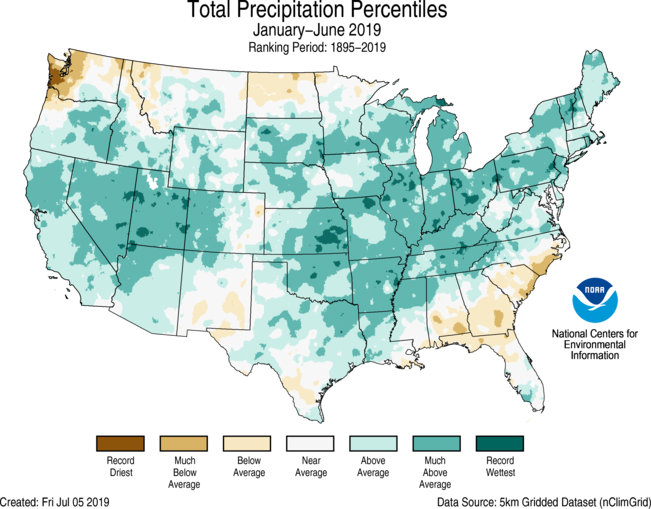
For the year-to-date 2019, the precipitation total was 19.05 inches, 3.74 inches above average, and the wettest such period in the 125-year record. Graphic: NOAA
Atmospheric Rivers boost snowpack
During the 2018-19 winter, atmospheric river events significantly increased snowpack in the Sierra Nevada and the Rocky Mountains. Both areas are key sources of water supply for the Southwest, including California and San Diego County.
Precipitation in the contiguous U.S. was above average from January to June 2019, according to a NOAA climate report released this week. The report said the 19.05 inches during the six-month period was 3.74 inches above average and the wettest such period in the 125-year record.
The January-to-June 2019 precipitation map showed California’s statewide precipitation was “above average” and “much above average.”