Efficient Irrigation Delivers Water While Protecting Plants
Due to the lack of rainfall in the San Diego region, even sustainable landscaping sometimes relies on artificial irrigation. Irrigation systems must be thoughtfully designed, installed, and programmed. Once in place, the many interconnected mechanical elements must be maintained properly for optimal performance.
“Irrigation efficiency” is a way of describing how well your irrigation system is doing its job delivering water for the beneficial use of the plants in your landscaping.
When irrigation system efficiency isn’t maximized, it can cause you to use more water than needed. Possible problems fall in three major categories: site conditions in your landscaping, irrigation control, and the uniform distribution of water by your irrigation system.
How to maximize irrigation impact

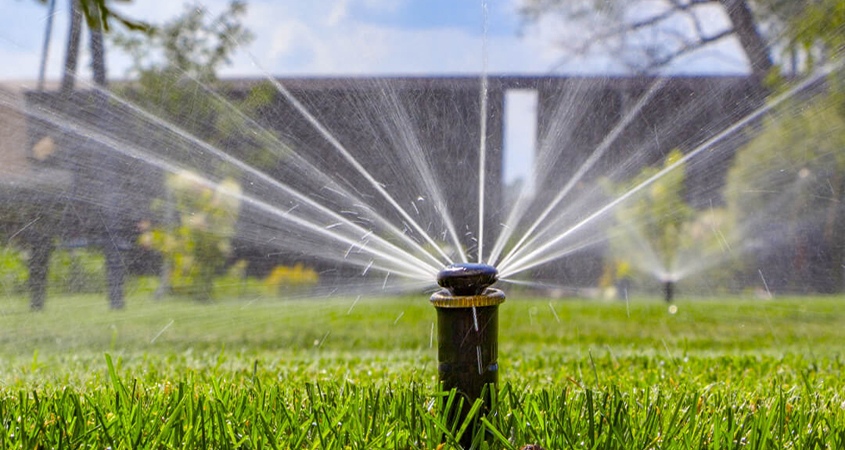
You may want to get help planning your irrigation system from a qualified professional. Photo: San Diego County Water Authority
There are three ways to improve your irrigation system efficiency:
- Smart Irrigation Management
- State of the Art System Upgrades
- Matching Irrigation to Your Hydrozones
Setting and forgetting your irrigation controller is a thing of the past. Even if you don’t have a “smart” irrigation controller to adjust your program for weather conditions, be more proactive in managing your watering, and more closely try to match your watering schedule with the actual water needs of your landscaping.
Upgrading your system with state-of-the-art components is a good investment and the single most significant thing you can do to save water.
Tips on professional help
You may decide to get professional help with your irrigation system. Look for designers or contractors qualified to provide these services. Credentials such as the Irrigation Association’s Certified Irrigation Designer designation can help assure your project will be successful. You can also ask if your contractor is a Qualified Water Efficient Landscaper (QWEL).
This article is part of a year-long series inspired by the 71-page Sustainable Landscapes Program guidebook. The Water Authority and its partners also offer other great resources for landscaping upgrades, including free WaterSmart classes at WaterSmartSD.org.